
Insights about the genetic and molecular mechanism is precondition to improve the clinical management and progress into novel therapeutic interventions. Currently, various susceptibility genes encoding various enzymes involved in the activation, cell-cycle pathways, circadian rhythm pathways and DNA damage and repair caused by smoke as well as genes involved in inflammatory and apoptosis processes have been studied extensively. Nevertheless, these genes are linked with multiple lung cancer pathways 9. Worldwide so far, more than 60 loci have been linked with lung cancer by GWAS and candidate gene approach. GWAS, transcriptome wide association study (TWAS) and CGA has proved to be significant approach in understanding the genetic complexity and heterogeneity of multifactorial disorders through association studies. Before the GWAS era, the identification and characterization of lung cancer loci has been quite limited. Lung cancer is the major global health burden contributing for more than million death worldwide. With this perspective, we evaluated twelve genetic variants of ten genes that are critically important and were previously associated with various cancers including lung cancer. It is noteworthy that such studies will provide the holistic view of genetic landscape of non-small cell lung cancer in population of Jammu and Kashmir, North India. This is the first ever genomic study from the region targeting the critical genes involved in the pathophysiology of non-small cell lung cancer. With this background, the variants in genes, which are critically important in various biological pathways like DNA damage and repair, invasion, metastasis, autophagy, circadian rhythm, apoptosis and signaling processes like TCF21, ERCC1, BRIP1, ARNTL, ERCC5, REV1, PIK3CA, CASC16, DDC, BCL2 were targeted. Genetic characterization of variants have attracted significant attention in current medical era as potential biomarkers for predicting disease susceptibility and therapeutic targets 8. With the successive GWAS, over the recent past more than 60 genetic loci have been found to be linked with NSCLC risk. Currently, candidate gene approach (CGA) and Genome wide association studies (GWAS) has confirmed to be significant tools in interpretation of genetic complexity and heterogeneity of these disorders through association studies. Despite making several efforts to enhance the 5 year survival rate of lung cancer patients, it remains 15–20%, the lowest of all cancers 7.
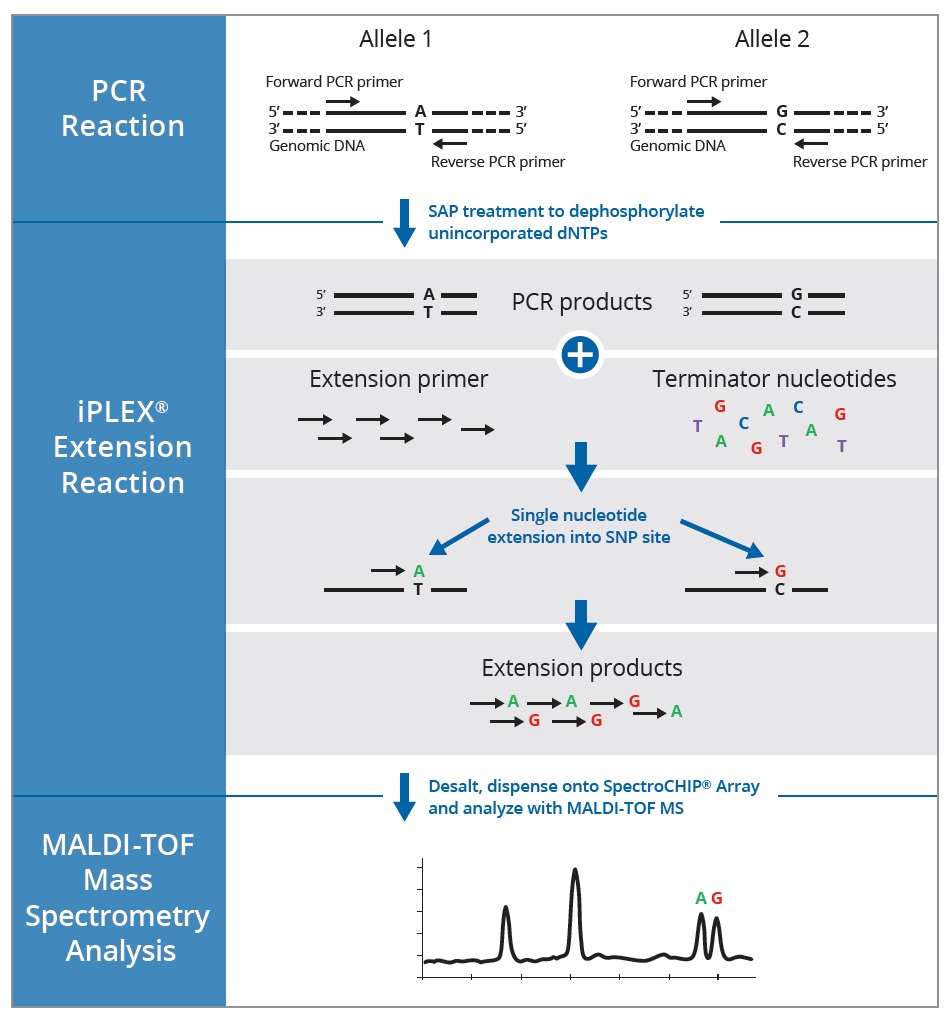
The study on the Kashmir region revealed that gastric carcinoma was commonly occurring cancer followed by lung carcinoma (9%) in general 6. The incidence of lung cancer and breast cancer is higher followed by esophageal cancer in Jammu region of J&K as reported by a recent study. Among North Indian region, Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) is at greater risk of death rate related to various cancers. In India, lung cancer is the chief cause of cancer-related mortality in both men and women 2 and its incidence is rising at an alarming rate accounting for 11.3% of all new cancers and 13.7% cancer associated death 3, 4, 5. It accounts for ~ 2.1 million new lung cancer cases and 1.8 million deaths worldwide 1. Lung cancer, a genetically heterogeneous disease is one of the leading causes of cancer incidence and mortality. It is further anticipated that such case control studies will help us in understanding the missing heritability of non-small cell lung cancer. In-silico findings of these genetic variants showed remarkable functional roles that needs in-vitro validations. With prospective case–control association study design, twelve variants from ten genes were evaluated. These genetic variants were selected from literature for their association with various cancers worldwide and this is the first study from the region to examine these critically important genetic variants. We performed multiplex PCR and genotyped twelve single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in 723 samples (162 NSCLC cases and 592 healthy controls). The present case–control association study focused on the cost effective high throughput genotyping using Agena MassARRAY matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight, mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) platform to analyze the genetic association of candidate genetic variants. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 80% of total lung cancer cases and 20% cases are Small cell lung cancer (SCLC).

Lung cancer is genetically diverse and a major health burden.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
